By the end of this unit you should:

Listen to and watch this review of logical arguments.
Simply put, reasoning can be thought of as the process used to move from evidence to claim, or from premises to conclusion. This course focuses on logical reasoning.
List the different types of reasoning that you know. Prepare to explain them to a classmate in English. Rehearse by saying each explanation aloud to yourself or practice with a classmate.
Watch this explanation of four types of reasoning.
Watch this excellent explanation of reasoning.
Listen to this explanation of terminology to describe statements, premises, cases, arguments and conclusions.
These are some of the main terms mentioned in the explanation.
One of the key aspects to remember is the relationship between reasoning and possible types of conclusions. Conclusions based on deductive reasoning may be sound or unsound. Conclusions based on inductive reasoning may be cogent or uncogent. Conclusions based on abductive reasons will be uncogent.
Identify the types of reasoning used in arguments created by the 2020 cohort on the topic of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Note that the premises may be true or false. The argument may be valid or invalid. Conclusions reached using deductive reasoning may be sound or unsound. Conclusions reached using inductive reasoning may be cogent or uncogent. Conclusions reached using abductive reasoning are uncogent.
Consider this diagram and the relationship between the different types of reasoning.
Although this section is not part of the official syllabus, it is important to understand that reasoning is not limited to deductive, inductive and abductive. Certainly, deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning are the two most commonly referred to types of reasoning.
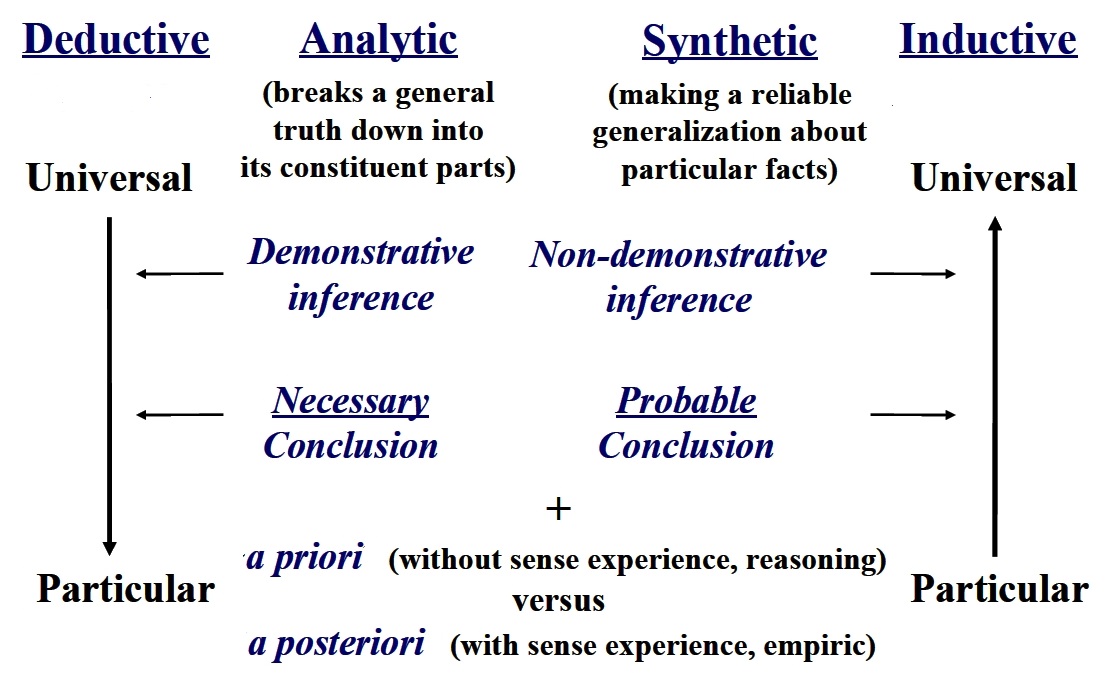
The different types of reasoning are listed below:
Knowledge and application activities are designed to help you activate the key terminology and apply the concepts covered in the course so far. Try to use the terminology and concepts accurately and appropriately.
Write three arguments related to the Olympics. Each argument must use a different form of reasoning. Avoid using false premises. For each argument, write a short explanation describing the premises, argument, reasoning and conclusion using logical terminology. Submit your work via ELMS.
Make sure you can explain the following 13 concepts in simple English:
Running count: 36 of 108 logical concepts covered so far.