By the end of this unit you should:

Answer the following questions.
If you delay tasks until later, and then rush to finish them before the deadline, you are not alone. This is a common strategy. If you delay tasks and then fail to finish them before the deadline, this is also common; but it unlikely to lead to success. This unit is designed to help you understand why people delay doing important jobs. The aim, of course, is to help you take action and complete your tasks on schedule.
Read.
Temporal discounting is the preference to receive a small reward soon rather than a larger reward later. Would you prefer to eat some cake now, or have a six-pack abs in the future? Would you prefer to check your Facebook or Instragram for five minutes now, or check them for longer tomorrow? For most people, the further away a reward is, the less likely it is chosen. Our brains resolve that it is better to get a small reward now than a larger reward later.
At the University of Aizu, many students choose to focus on playing online games and enjoying life now, but the downside is that some will never graduate and will not get the reward of a degree, better job and better future. Make sure you make good choices about which rewards are important and how you allocate time.
Watch this video clip to understand how dopamine affects behaviour (7 min 35 sec).
Read.
Temporal discounting is the preference to receive a small reward soon rather than a larger reward later. Would you prefer to eat some cake now, or have a six-pack abs in the future? Would you prefer to check your Facebook or Instragram for five minutes now, or check them for longer tomorrow? For most people, the further away a reward is, the less likely it is chosen. Our brains resolve that it is better to get a small reward now than a larger reward later.
Try the Pomodoro technique with a virtual study buddy (2 hours comprising 4 cycles of 25 min study, 5 min rest).
Read.
One way to harness the effect of dopamine, is to us the Pomodoro technique. In short, you allocate a fixed period of time to work, e.g. 25 minutes and then as a reward for completing this, you reward yourself with a shorter period of "fun" time, e.g. 5 minutes. A typical example would be to study for 25 minutes and then spend 5 minutes checking SNS. This technique only works when you use a timer and you stick to the times.
Read.
There are two types of deadlines: External or immovable deadlines, and internal flexible deadlines. For larger projects, it is often necessary to breakdown the task into small sections. For each section, setting yourself a deadline can increase the chance of completing the project on time. A Gantt chart makes it easy to see which tasks need to be completed and shows the sequence of tasks. Gantt charts help you identify potential bottlenecks or problems in the sequencing of tasks.
Watch this video to understand more about Gantt charts (3 min 27 sec).
Read.
Everyone is different, so you need to select the best combination of choices for yourself. Some things (motivators) positively affect motivation and some things (demotivators) negatively affect motivation 'motivators'. List the things that distract you for your work and study. How can you overcome these? List the things that motivate you. Can you use them next time your work or study?
This is an example list of suggestions:

The ostrich effect is a tendency to ignore important information when we feel overwhelmed, stressed or worried.
Create a Gantt chart for your graduation thesis, and submit the image file through Slack.
Below is an example of a Gantt chart.
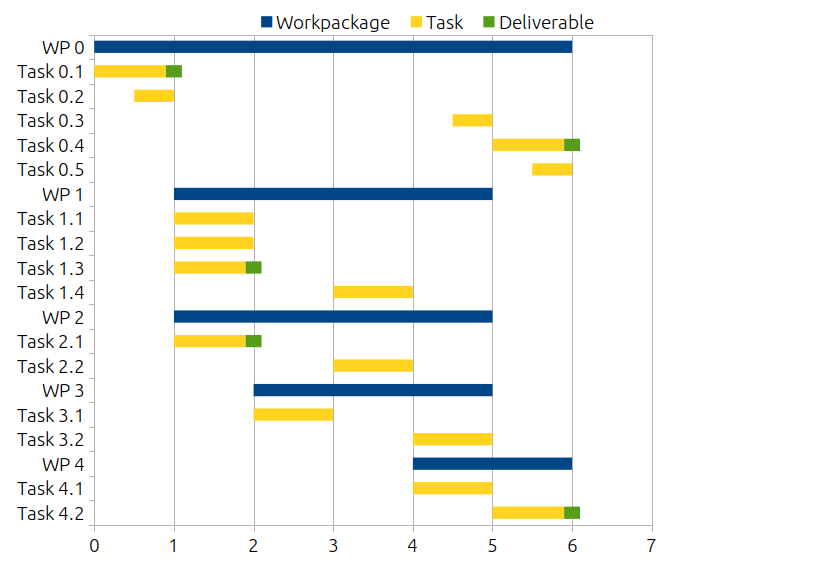
Source: Wikipedia Commons
Make sure you know the meaning of the following terms: