By the end of this unit you should:

Work in pairs to decide which of the following items may be classified as educational technology.

Read.
There are multiple definitions of educational technology, and so what is means or does not mean depends on your operational definition. It should be noted that what is categorized as a technology changes with time, and what counts as educational also varies with context. However, for the moment, let's use the definition as described by the Association for Educational Communications and Technology (AECT): namely that: educational technology is:
"the study and ethical practice of facilitating learning and improving performance by creating, using and managing appropriate technological processes and resources".Source: Richey, R.C. (2008). Reflections on the 2008 AECT Definitions of the Field.TechTrends, 52(1),24–25.
Simply put, nowadays educational technology is considered to be the use of hardware and software for practice or learning. As with definitions, there are numerous taxonomies that can be adopted to classify educational technology into different subcategories. In this course, we will focus on the following categories:
Work in pairs. Check your understanding of the terms and try to name an example technology for each category.
Five main learning theories in education are: behaviourism, cognitivism, constructionism, social constructionism, and connectivism.
Although there are many theories of learning, the three most well-established theories are: behaviourism, cogntivism and constructionism. Social constructinism and connectivism, are more recent developments.
Click on the name of the categories of educational technology for a description and selected examples. Texts were generated by ChatGPT-4.
Learning Management Systems help educators organize, deliver, and manage instructional content and resources, as well as monitor student progress and engagement. Examples include Canvas, Moodle, and Blackboard.
Multimedia and Interactive Learning Resources use a combination of text, images, audio, video, and interactive elements to create engaging and immersive learning experiences. Examples include BrainPOP, BBC Bitesize, and the National Geographic Education Portal.
Content Authoring Tools allow educators to create, edit, and publish multimedia learning materials, such as interactive lessons, quizzes, and simulations. Examples include Adobe Captivate, Articulate Storyline, and iSpring Suite.
Collaboration and Communication Tools enable communication and collaboration between students, educators, and peers, often in real-time. Examples include Google Workspace for Education, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom.
Assistive Technology tools support learners with disabilities, enabling them to access, engage with, and succeed in educational environments. Examples include screen readers, speech-to-text software, and alternative input devices.
Virtual Learning Environments (VLE) and Virtual Classrooms: These platforms provide digital spaces where educators and learners can interact, collaborate, and access learning materials in a virtual setting. Examples include Edmodo, Adobe Connect, and WizIQ.
Mobile Learning and Mobile Apps leverage the ubiquity and portability of mobile devices to provide learning experiences that can be accessed anytime, anywhere. Examples include Duolingo, Khan Academy, and TED-Ed.
Game-Based Learning and Gamification approaches integrate game elements and mechanics into the learning process, either through educational games or by adding game-like features to traditional learning activities. Examples include Minecraft: Education Edition, Classcraft, and Quizizz.
Educational technology covers many different subject domains. However, on this course, we are particularly focussed on educational technology that is related to language learning.
Watch this short introduction to Moodle, an open-source LMS.
The developers of Moodle published their education philosophy available here over 20 years ago. The wording has changed slightly over the years but the general focus is the same.
Read the following paragraph.
This course is designed to serve as a multimedia and interactive learning resource. Rather than a text only course, image, audio and video files are used. Interactivity with the materials is achieved by drawing on event managers to control behaviour in the website, while server-side interactivity is faciliated using the LMS rather than this website.
Discuss the extent to which the paragraph is accurate. Suggest ways in which the course may be improved in terms of its multimedia and interactive content.
Check out this resource designed to introduce developers to Storyline, one of the many content authoring tools..
Zoom, Google meet and Teams are three popular collaboration and communication tools.
Ask and answer questions about these tools.
The primary purpose of assistive technologies is to help people who otherwise would have difficulties understanding spoken or written materials. People with impaired vision (e.g. blind) may find it difficult or impossible to read text on the internet. However, it is possible to help such users by, for example:
Discuss how any of these technologies may be used in a language learning context.
Virtual learning environments share many similiarites with LMSs. However, there are some differences.
Spend a few minutes searching the web for reliable sources to discover the differences between VLEs and LMSs. Discuss your findings with a partner
Watch to understand the four different types of language learning apps.
Game-based Learning and gamification does not only mean using games to learn. We can use various aspects of gamification to motivate learners (and ourselves).
Paul Gee is one of the gamification gurus. He identified a set of principles for game-based learning. Check out the principles here. The chart below provides a visual summary of the key gamification concepts.
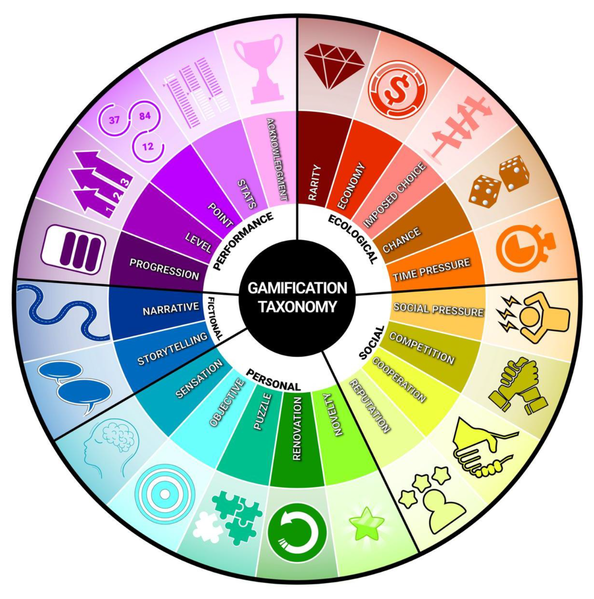
Source: Wikimedia Commons.
Can you:
If you cannot, make sure that you do before your next class.
Running count: 19 of 65 concepts covered so far.