By the end of this unit you should:

Work in pairs. Without reading your notes or the course website, describe what an expert system is. Remember to use the technical terms you learnt in the previous unit.
Identify the relationship between the three categories of knowledge described.
Knowledge may be classified by category. The category of knowledge is not the domain, discipline or subject. In this course, we will focus on three categories of knowledge, namely: explicit, tacit and implicit.
Explicit knowledge is written, implicit has not been written but easily be while tactic knowledge is difficult to write down since even the expert may not know how to describe what they know and can do.
Work in pairs. Discuss the category of knowledge for each of the examples below.
Explicit knowledge
Tacit knowledge
Implicit knowledge
Implicit knowledge
Tacit knowledge
Explicit knowledge
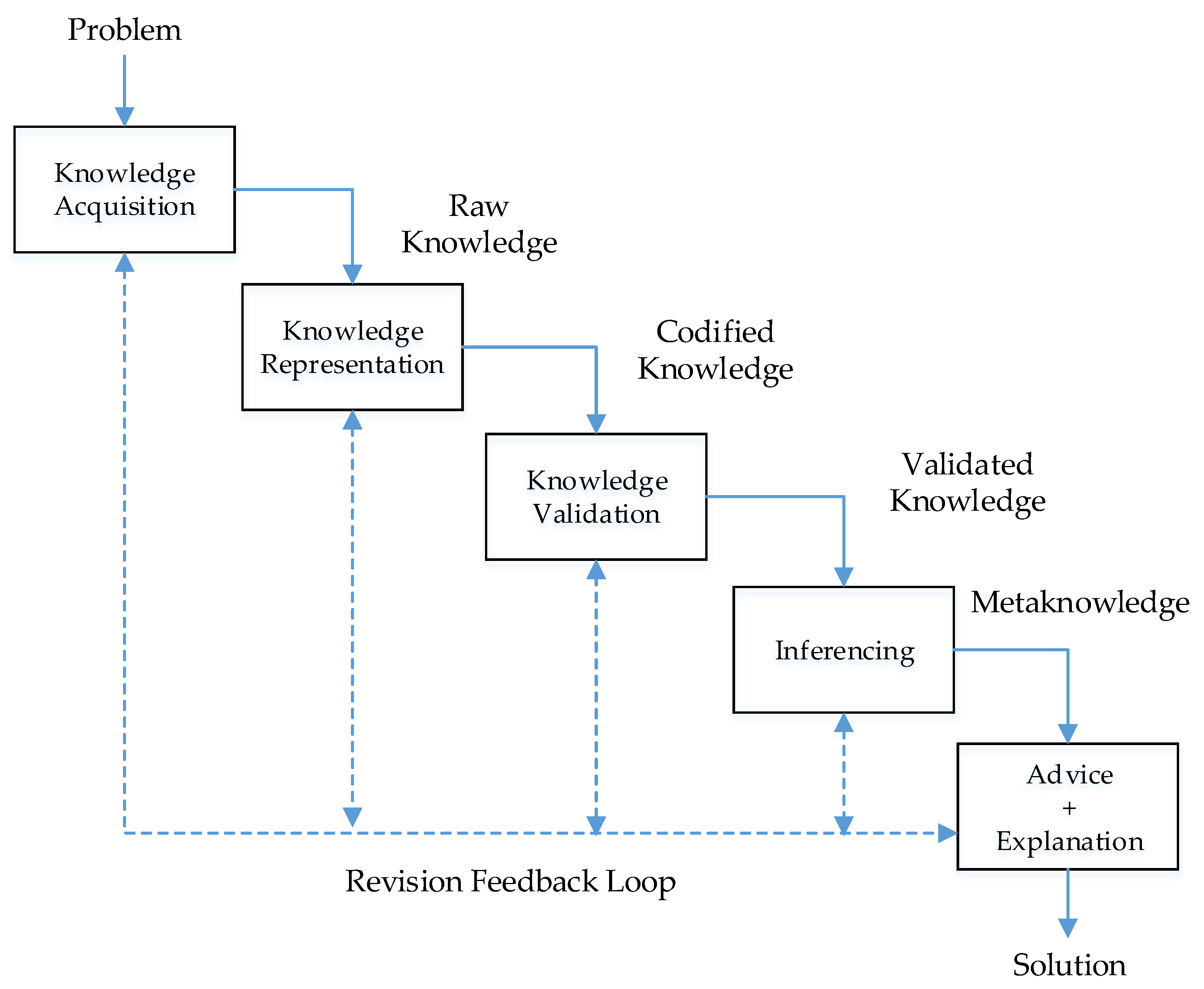
Read to understand five phases in the knowledge engineering process.
This is the process of obtaining information from human experts or other credible sources. The data could be about a specific domain, like medical diagnosis, financial forecasting, or weather prediction. This is usually the most time-consuming part of knowledge engineering because it involves extensive interaction with domain experts and often a careful examination of complex domain knowledge.
Once the data is obtained, it must be represented in a way that the system can understand. This could be through rule-based systems, semantic networks, frames, or other methods. The choice of representation may affect the ease of learning, the speed of inference, and the system's capabilities.
It refers to how the expert system applies logic to the knowledge it has been given to arrive at new conclusions or solutions. Depending on the complexity of the problem, this might involve straightforward logical deductions or more complex reasoning methods.
This involves testing the system to ensure that it's using its knowledge correctly. This is a critical step for verifying that the system provides correct and reliable outputs.
This is an ongoing process that ensures the knowledge within the system remains accurate and up to date. As new information becomes available or as the field of knowledge progresses, the system should be updated and refined.
Read this description to discover the number of methods of knowledge acquisition.
Knowledge acquisition, crucial in the development of expert systems, can be achieved through both non-digital and digital methods. Non-digital methods include interviewing, observation, analysis of documented information, and protocols and scenarios. Interviewing and observation involve direct interaction with domain experts to understand their decision-making process and methodology. Analysis of documented information involves extracting knowledge from existing resources like manuals, documents, or instructional videos. Protocols and scenarios entail presenting experts with hypothetical situations or problems to evaluate their problem-solving approach. On the other hand, the digital method includes machine learning, where systems learn from large datasets rather than relying on explicit programming. The system is trained, evaluated, and tuned based on a relevant dataset, enabling the model to make predictions or decisions without human intervention. These methods, employed based on the specific context and requirements, facilitate capturing knowledge from various sources, subsequently contributing to the creation of effective expert systems.
Read the AI-generated descriptions of the following types of knowledge representation. Search online, Use DeepL or refer to ChatGPT to better understand the types that are more difficult to comprehend.
Work in pairs. Discuss the type of knowledge representation for each of the examples below.
Rule-based systems
Conceptual graphs
Production systems
First order logic
Fuzzy logic
Frames
Semantic networks
Bayesian networks
Can you:
If you do not, make sure that you do before your next class.
Running count: 30 of 30 concepts covered so far.