- ベンチャー体験工房3
- Developing a Novel Pattern Mining Model to Discover Hidden Patterns in Fukushima Traffic Congestion Big Data
- - Japan Road Transportation Information Center (JARTIC) has set up the sensor network to monitor traffic congestion in Fukushima.
- Each road-segment in this network generates data at every 5-minute interval.
- Previous year, we have developed a data warehouse technology that generates data frames at 10 times faster than the state-of-the-art.
- This year, we plan to develop a novel pattern algorithm to discover hidden patterns. - シラバス詳細
2025年4月
4月7日
Introduction to Traffic Information Systems: Understanding JARTIC and TCSS
授業内容:We covered the role of the Japan Road Traffic Information Center (JARTIC) and the Traffic Congestion Statistical System (TCSS). We explored how JARTIC collects and distributes traffic information through 133 centers nationwide. The importance of real-time traffic data for road users was highlighted.

4月14日
Data Collection Techniques: Sensors and Measurement Points
授業内容:We learned about the data collection process using sensors installed at over 40,000 measurement points. The types of sensors, such as ultrasonic vehicle detectors, and the significance of collecting traffic volume and occupancy time every 5 minutes were thoroughly analyzed.

4月21日
Real-Time Traffic Analysis: Interpreting Congestion Data
授業内容:This class focused on the processing and interpretation of live traffic data, including the classification of congestion status into traffic jam, congestion, no congestion, and unknown (sensor abnormality). We practiced accessing this data through the TCSS interface.

2025年5月
5月5日
授業内容: Temporal and Spatial Resolution of TCSS Data :
Analyzes how TCSS offers high-resolution temporal (5-minute intervals) and spatial (road link-level and mesh code) data. This granularity allows researchers to study traffic dynamics over time and space with precision.
5月12日
授業内容:Congestion Detection and Classification Algorithms in TCSS:
Focuses on the definitions and criteria used to detect and classify congestion. It explains how TCSS uses speed thresholds and vehicle detection data to classify congestion into levels such as "light" or "heavy" across various road types.
5月19日
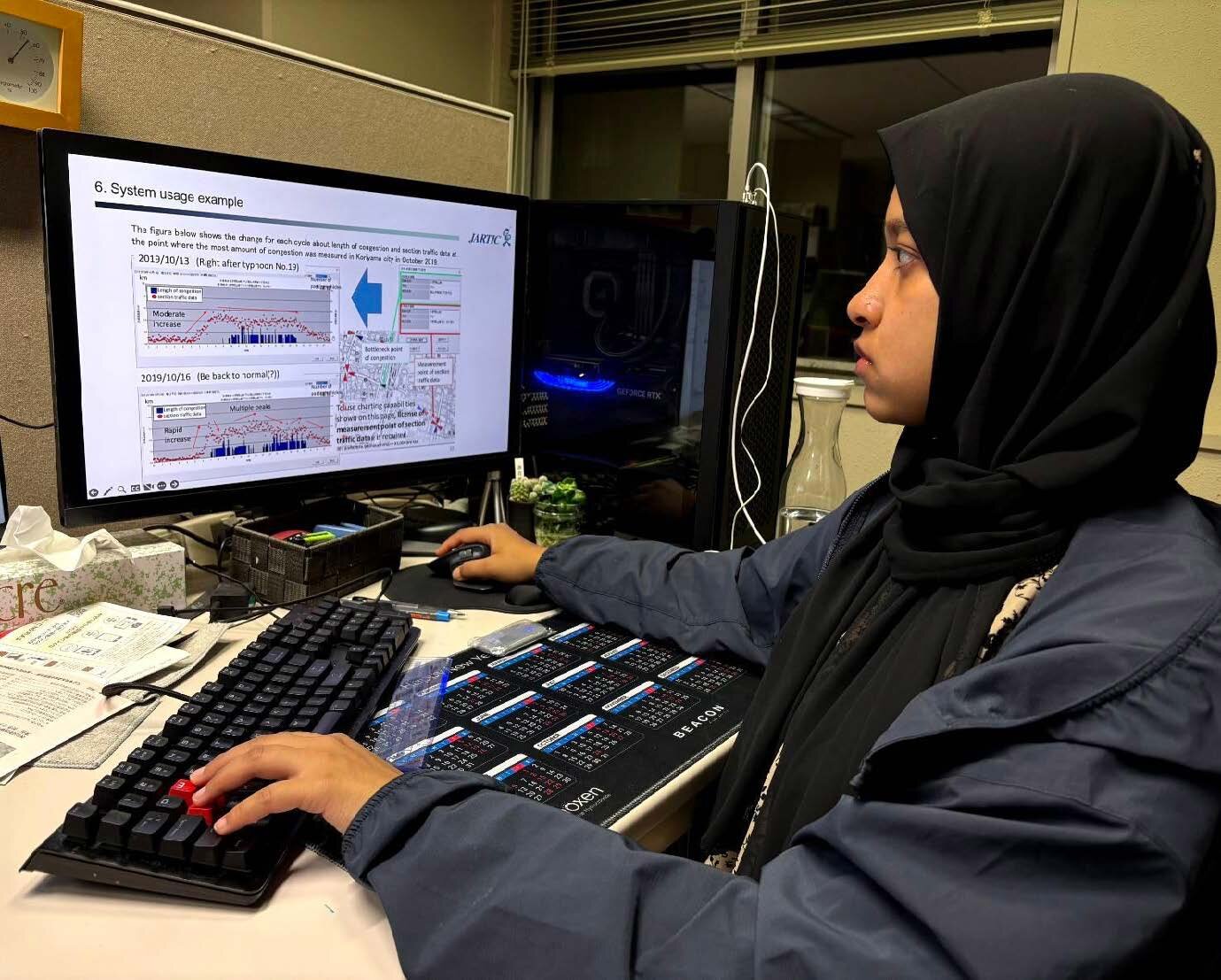
授業内容:Visualization Techniques: Mapping and Graphical Representation in TCSS.
Details the system's ability to visualize traffic data through interactive maps, Excel tables, and statistical graphs. It discusses how these visualization features support both operational monitoring and academic research.

2025年6月
6月2日
授業内容:Traffic Data Normalization and Anomaly Handling:
We removed unnecessary unnamed columns, detected abnormal traffic values, and applied threshold-based normalization to standardize the dataset for modeling.

6月9日
授業内容:Missing Value Imputation in Traffic Datasets:
We explored multiple imputation techniques--mean, median, mode, KNN, forward fill, and backward fill--to handle missing data. After evaluation, mean imputation was selected as the best method.

6月16日
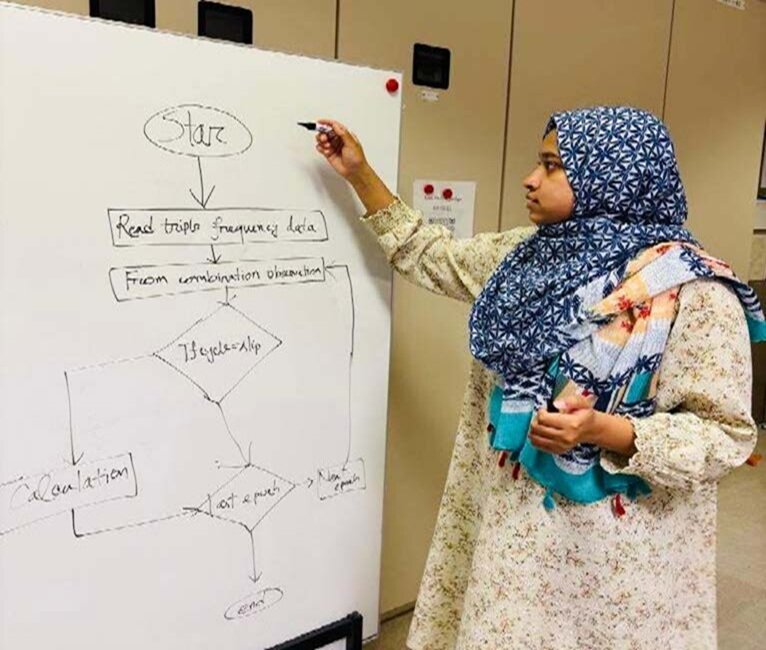
授業内容:Deep Learning Models for Traffic Forecasting:
We experimented with various time-series deep learning models including LSTM, Bi-LSTM, GRU, Autoencoders, Transformers, and CNNs to predict traffic patterns.

6月23日
授業内容:LSTM-Based Traffic Flow Prediction:
We implemented an LSTM model that performed well due to its layered architecture and ability to capture long-term dependencies in traffic data.
2025年7月
7月7日
授業内容:Conducted an exploration of forecasting models for traffic data. Studied the working mechanisms of various models and how they process traffic information. Analyzed how data flows through multiple layers in deep learning architectures, ocusing on preprocessing, feature extraction, and prediction.

7月14日
授業内容:Implemented a deep learning model for traffic data prediction using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. Designed the architecture of the deep learning model including input, hidden, and output layers. Focused on capturing temporal dependencies in traffic data using sequential modeling.
7月21日
授業内容:Developed and implemented time-based forecasting techniques. Evaluated the model performance over various time intervals to improve forecasting accuracy. ocused on daily and hourly traffic patterns for better resolution in predictions.

7月28日
授業内容:Worked on a multi-task learning model to enhance traffic data forecasting. Designed and compared multiple models to handle different forecasting tasks simultaneously. Finalized and selected the best-performing model based on accuracy and generalization performance.

2025年10月
10月6日
授業内容:
•Learning to use Jartic road traffic software to understand its data acquisition process.
•Collecting traffic data from the platform for further analysis.
•Gaining insights into traffic flow patterns and congestion trends through data exploration.


10月20日
授業内容:
•Learning to use the Macro Recorder software for automating repetitive tasks.
•Collecting all available traffic data for comprehensive analysis.
•Preparing the dataset for further processing and pattern identification.

10月27日
授業内容:
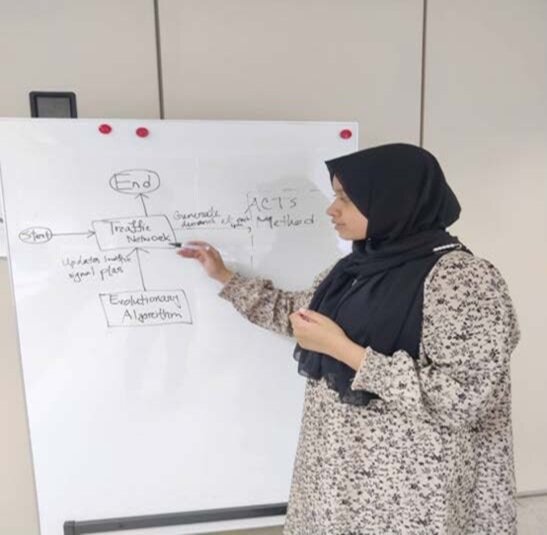
•Studying pattern mining techniques to analyse traffic congestion trends.
•Exploring algorithms that identify frequent and time-dependent congestion patterns.
•Aiming to uncover insights for improving traffic flow and management.

2025年11月
11月4日
授業内容:
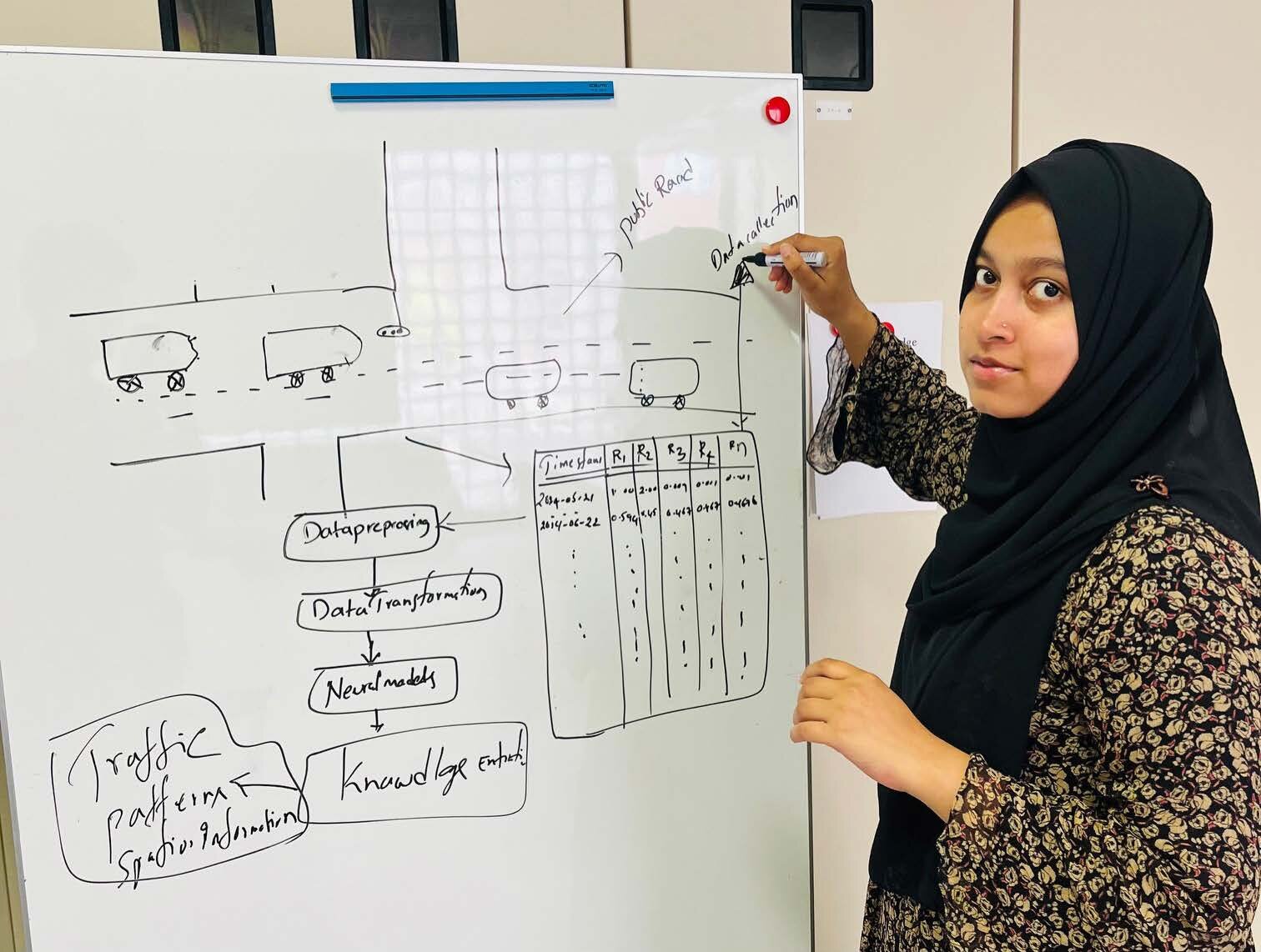
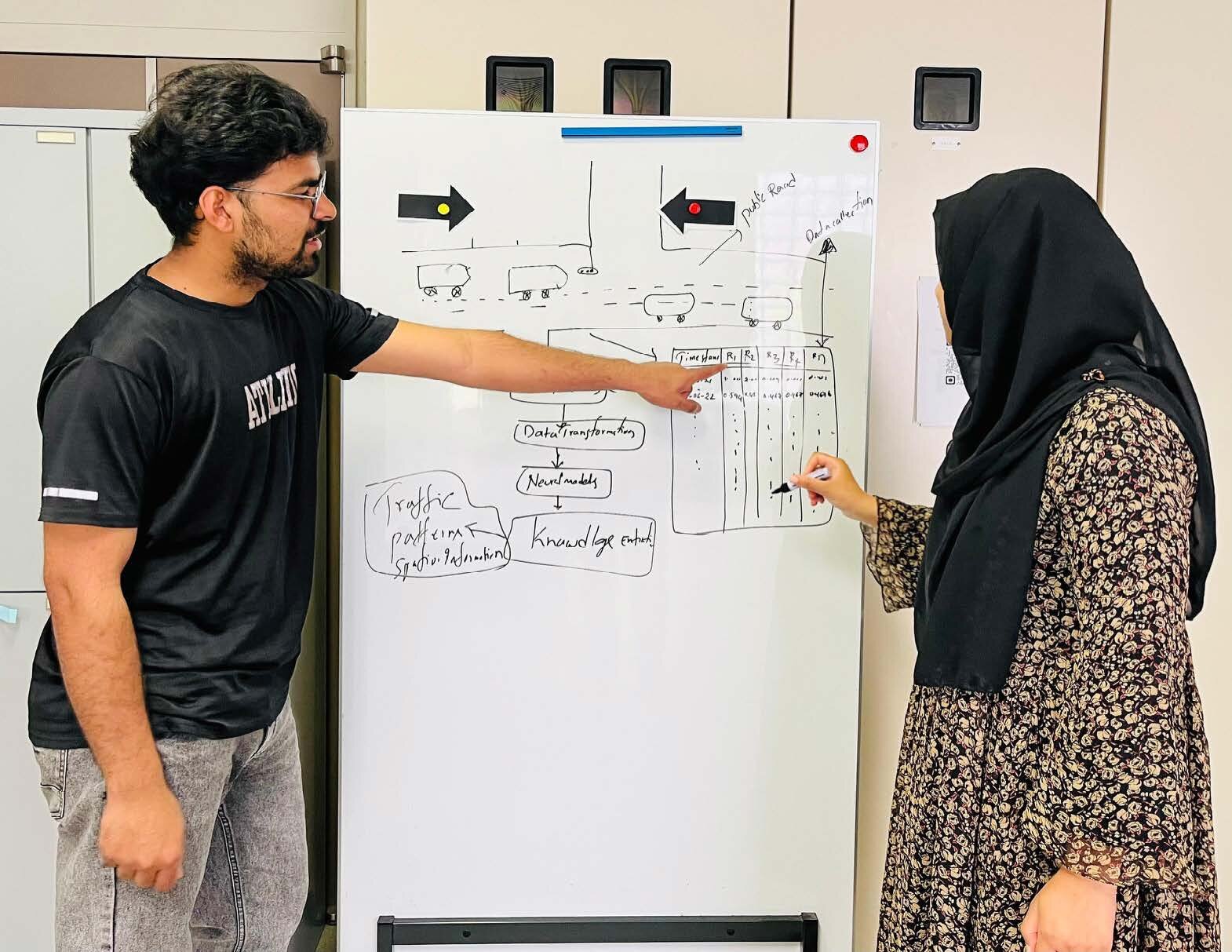
•Process the traffic dataset to ensure consistency, completeness, and readiness for symbolic conversion.
•Analyze the key attributes of the traffic data to determine which features require symbolic abstraction.
• Design an appropriate symbolic representation schema for transforming raw numerical and categorical traffic values into symbolic forms.

11月10日
授業内容:
•Implement the transformation process that converts the preprocessed traffic data into a symbolic dataset.
•Identify patterns and relationships in the dataset that guide the learning of symbolic transformation rules.
•Learn and formalize the rules that map raw traffic features into higher-level symbolic constructs.

11月17日
授業内容:
•Develop symbolic temporal rules that capture dynamic changes and time-dependent behavior within the traffic data.
•Study knowledge graph principles to understand how symbolic and temporal relationships should be modeled in a graph structure.
•Construct a knowledge-graph-ready dataset that aligns with graph database requirements for efficient querying and reasoning.

2025年12月
12月8日
授業内容:
•Analyse spatial characteristics of the traffic network to identify location-based patterns and relationships.
•Define symbolic spatial representations that capture road topology, intersections, regions, and proximity relationships.
• Develop spatial transformation rules that encode geographic and structural dependencies in traffic data.

12月15日
授業内容:
•Formulate symbolic traffic behaviour rules that represent congestion, flow variation, and abnormal events.
•Integrate spatial, temporal, and traffic behaviour rules into a unified rule framework.

12月22日
授業内容:
•Implement a single, cohesive rule-based transformation pipeline that applies all learned symbolic rules.
•Apply the integrated transformation framework to the entire traffic dataset.
•Generate the final transformed traffic dataset that captures spatial, temporal, and behavioural semantics in symbolic form.

2026年1月
1月5日
授業内容:
•Study the architecture and core principles of graph databases to understand node-relationship-based data modelling.
•Analyse Neo4j's data model, query language (Cypher), and indexing mechanisms for efficient graph querying.

1月19日
授業内容:
•Design appropriate node types and relationship schemas for representing the transformed symbolic traffic dataset.
•Define and formalise relationships among spatial, temporal, and traffic behavior entities within the graph structure.
•Install and configure the Neo4j graph database environment for system implementation.

1月26日
授業内容:
•Prepare the transformed symbolic traffic dataset in a format compatible with Neo4j (e.g., CSV or structured import format).
•Load the dataset into Neo4j by creating nodes and establishing the predefined relationships using Cypher queries.Implement a user query interface that retrieves relevant answers by combining graph database results with Gemini-based reasoning.

2026年2月
2月2日
授業内容:
•Validate the graph structure to ensure correctness, consistency, and completeness of the imported data.
•Integrate the Neo4j database with the Gemini API to enable intelligent query processing and semantic interpretation.
•Implement a user query interface that retrieves relevant answers by combining graph database results with Gemini-based reasoning.



