By the end of this unit you should:

Read.
This unit aims at helping you understand more about using Python for natural language processing (NLP). All computer science majors learn C and Java in their first and second year at the University of Aizu. Many students also learn C++. This means that concepts such as lists, arrays and loops should need no explanation.
Take this online quiz from W3 Schools to assess how much or how little you need to study to be able to write a program in Python.
Watch this short introductory video.
This introductory video (6 mins 41 secs) covers the basics in slightly over five minutes. This video is probably too fast for those new to programming, but is suitable for those who already know what operators, lists and loops are.
Work in pairs or threes. Name and explain the difference between the following data types.
["apple","banana","carrot"]{"apple","banana","carrot"}{"food": "banana","colour": "yellow"}("apple","banana","carrot")Check your answers online.
Note that to work with arrays in Python, you have to import a library. The most popular library for this is NumPy.

Read this to understand the concepts of NLP, POS tags and parse trees.
A natural language processing (NLP) system is usually called an NLP pipeline. This because it usually involves several stages (steps or layers) of processing. The pipeline is one directional. There is an input (natural language) and an output (processed text). Simply put, NLP is applying artificial intelligence to human languages.
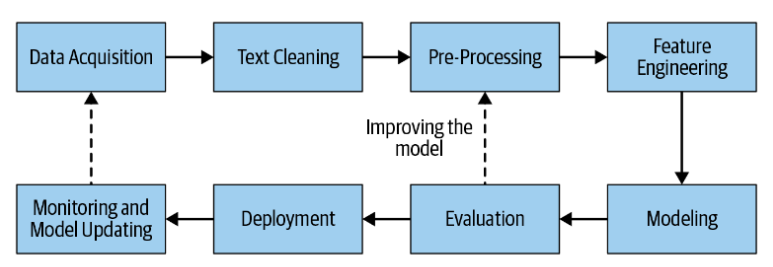
POS tagging is the act of labelling words with a particular part of speech. The common parts of speech are noun, verb, adverb and adjective. However, most POS taggers use a much large set of tags. The most popular POS tagset has 36 tags. NLP pipelines that aim to map syntax or disambiguate meanings often use this layer. The Penn treebank tagset is shown in the table below.
| CC Coordinating conjunction | CD Cardinal number | DT Determiner |
| EX Existential there | FW Foreign word | IN Preposition or subordinating conjunction |
| JJ Adjective | JJR Adjective, comparative | JJS Adjective, superlative |
| LS List item marker | MD Modal | NN Noun, singular or mass |
| NNS Noun, plural | NNP Proper noun, singular | NNPS Proper noun, plural |
| PDT Predeterminer | POS Possessive ending | PRP Personal pronoun |
| PRP$ Possessive pronoun | RB Adverb | RBRAdverb, comparative |
| RBS Adverb, superlative | RP Particle | SYM Symbol |
| TO to | UH Interjection | VB Verb, base form |
| VBD Verb, past tense | VBG Verb, gerund or present participle | VBN Verb, past participle |
| VBP Verb, non-3rd person singular present | VBZ Verb, 3rd person singular present | WDT Wh-determiner |
| WP Wh-pronoun | WP$ Possessive wh-pronoun | WRB Wh-adverb |
If you are keen on learning this tagset. Try out this timed game.
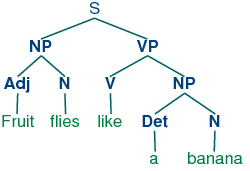
NLP pipelines can be used for many tasks. Dependency parsing is one task that is often used as one step or layer. Dependency parsing uses the part-of-speech tags assigned to words in a previous layer and creates a parse tree. The parse tree identifies a sentence and splits up the sentence sequentially. This shows the relationship between the words. During this process, trees of parent and child words are created. Parse trees are used in many NLP tasks. However, it needs to be remembered that any errors in the POS tags will affect the accuracy of the parse tree. The example below shows how a simple sentence can be broken down and the relationship between individual words mapped out on to a parse tree.
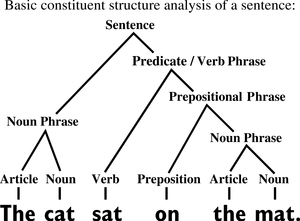
Source: Wikicommons
The Natural Language Tool Kit (NLTK) is one of the most popular libraries for creating NLP pipelines. There are many tutorials online to show you how to get started. For those who prefer a video introduction, check out the first video in this playlist. The topic is tokenizing. Sentdex is a popular programming YouTuber with over a million subscribers.
Watch and listen to this short introducttion to using NLTK with Python.
Work in a group. Each group will be allocated a topic. Learn your assigned topic and prepare to explain the topic.
Cross group and explain your topic to students who have prepared a different topic. Change groups and repeat.
Listen in English to the explanations of the Python code created by Jonathan Dunn, which is available on GitHub. These explanations were created by students in Spring 2022. If you find any errors, please notify your tutor.
If you prefer, you can also listen to explanations of the code in Japanese.
Read the pseudocode and compare it to the Python code.
PseudocodeRetrieve the number to be reversed from the user into variable sample_number.
Initialize the temporary variable test_number as zero.
Perform a while loop until the sample_number variable is greater than zero.
Modulus the sample_number variable by 10 and store the remainder.
Multiply the temporary number of test_number by 10 and add the returned value to the remainder.
Print the generated test_number onto the console.
Python codesample_number = int(input("Number to be reversed: "))
test_number = 0
while(sample_number>0):
remainder_number = sample_number % 10
test_number = (test_number * 10) + remainder_number
sample_number = sample_number//10
print("Value after reverse : {}".format(test_number))
Source: Python Tutorial on Educaba .
Work alone, but feel free to ask your friends for help. Practice using Python for some natural language programming tasks. You can use Terminal, any IDE, or an online compiler. Copy and paste the code into the submission form.
Describe your assigned authorship marker. Compare its usage with another related authorship marker. Write in plain language the steps needed in an program to automatically analyze your assigned language marker. Your code needs to identify, classify, count, compare and generate a value for the authorship feature. Work in a team. Only the team leader needs to submit the pseudocode and the Python program to ELMS.
Your assigned task is given below.
Describe your NEW assigned authorship marker. Compare its usage with another related authorship marker. Write in plain language the steps needed in an program to automatically analyze your assigned language marker. Adapt your original code submitted for Activity 10. Your code needs to identify, classify, count, compare and generate a value for the authorship feature. Work in a team. Only the team leader needs to submit the pseudocode and the Python program to ELMS.
Your assigned task is given below.
Make sure you can explain the differences between the following in simple English:
Running count: 58 of 60 concepts covered so far.