HAMEED Saji N.
Professor
- Affiliation
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering/Division of Computer Science
- Title
- Professor
- saji@u-aizu.ac.jp
- Web site
- http://enformtk.u-aizu.ac.jp/
Education
- Courses - Undergraduate
- Numerical Analysis, Dynamics
- Courses - Graduate
- High Performance Computing, Numerical Ocean-Atmosphere Modeling using OpenCL, Computational Fluid Dynamics
Research
- Specialization
-
Others
Climate Dynamics
- Educational Background, Biography
- PhD (Atmospheric Sciences), Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India
- Current Research Theme
- Climate dynamics
- Key Topic
- Numerical Modeling, Super El Nino, Indian Ocean Dipole
- Affiliated Academic Society
Main research
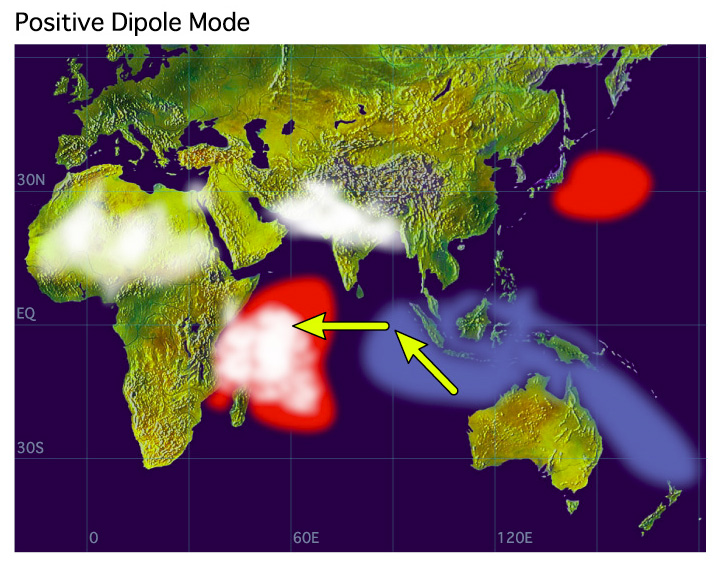
- Indian Ocean Dipole
-
The Indian Ocean Dipole is a climate phenomenon that affects global climate. It is an irregular oscillation with positive and negative phases. In the positive phase, sea surface temperatures of the eastern Indian Ocean experience unusual cooling. This is soon followed by a warming of sea surface temperatures in the western Indian Ocean. These changes lead to a large shift in rainfall from the eastern towards the western Indian Ocean, and is consequently associated with drought in the eastern and floods in the western Indian Ocean.
We study the mechanisms by which the Indian Ocean Dipole is generated using computer models. Areas of research include Indian Ocean Dipole dynamics, its impacts on global climate and how it interacts with the El Nino Southern Oscillation.
- Super El Nino
-
What processes are responsible for Super El Ninos are explored using computational modeling approaches.
Dissertation and Published Works
| 1. | Title: A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Goswami, B. N.; Vinayachandran, P. N.; et al. Source: Nature Volume: 401 Pages: 360-363 Published: 1999 Times Cited: 1582 DOI: 10.1038/43855  | added 24-May-10 |
| 2. | Title: Possible Impacts of Indian Ocean Dipole Mode events on global climate Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Yamagata, T. Source: Climate Research Volume: 25 Pages: 151-169 Published: 2003 Times Cited: 259 DOI: 10.3354/cr025151  | added 24-May-10 |
| 3. | Title: Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Indian Summer Monsoon Author(s): Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Saji, N. H.; et al. Source: Journal of Climate Volume: 17 Pages: 3141-3155 Published: 2004 Times Cited: 145 DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2004)0172.0.CO;2  | added 24-May-10 |
| 4. | Title: Structure of SST and surface wind variability during Indian Ocean Dipole Mode events : COADS observations Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Yamagata, T. Source: Journal of Climate Volume: 16 Pages: 2735-2751 Published: 2003 Times Cited: 131 DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)0162.0.CO;2  | added 24-May-10 |
| 5. | Title: Role of Narrow Mountains in Large Scale Organization of Asian Monsoon Convection Author(s): Xie, S. P.; Xu, H.; Saji, N. H.; et al. Source: Journal of Climate Volume: 19 Pages: 3420-3429 Published: 2006 Times Cited: 108 DOI: 10.1175/JCLI3777.1  | added 24-May-10 |
| 6. | Title: Response of the equatorial Indian Ocean to an unusual wind event during 1994 Author(s): Vinayachandran, P. N.; Saji, N. H.; Yamagata, T. Source: Geophysical Research Letters Volume: 26 Pages: 1613-1616 Published: 1999 Times Cited: 102 DOI: 10.1029/1999GL900179  | added 24-May-10 |
| 7. | Title: Tropical Indian Ocean Variability in the IPCC 20th-century climate simulations Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Xie, S. P.; Yamagata, T. Source: Journal of Climate Volume: 19 Pages: 4397-4417 Published: 2006 Times Cited: 78 DOI: 10.1175/JCLI3847.1  | added 24-May-10 |
| 8. | Title: Comments on "Dipoles, Temperature Gradients, and Tropical Climate Anomalies" Author(s): Yamagata, T.; Behera, S. K.; Rao, S. A.; et al. Source: Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society Volume: 84 Pages: 1418-1422 Published: 2003 Times Cited: 53 DOI: 10.1175/BAMS-84-10-1418  | added 24-May-10 |
| 9. | Title: Comments on "A Cautionary Note on the Interpretation of EOFs" Author(s): Behera, S. K.; Rao, S. A.; Saji, N. H.; et al. Source: Journal of Climate Volume: 16 Pages: 1087-1093 Published: 2003 Times Cited: 42 DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)0162.0.CO;2  | added 24-May-10 |
| 10. | Title: Satellite observations of intense intraseasonal cooling events in the tropical south Indian Ocean Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Xie, S. P.; Tam, C. Y. Source: Geophysical Research Letters Volume: 33 Published: 2006 Times Cited: 35 DOI: 10.1029/2006GL026525  | added 24-May-10 |
| 11. | Title: Indian Ocean Dipole Mode events and austral surface temperature anomalies Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Ambrizzi, T.; Ferraz, S. E. T. Source: Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Volume: 39 Pages: 87-101 Published: 2005 Times Cited: 33 DOI: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2004.10.015  | added 24-May-10 |
| 12. | Title: Processes and boreal summer impacts of the 2004 El Nino Modoki: An AGCM study Author(s): ASHOK, K; IIZUKA, S; RAO, SA; et al. Source: GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Volume: 36 Published: 2009 Times Cited: 25 DOI: 10.1029/2008GL036313  | added 29-Jul-09 |
| 13. | Title: Mechanisms of South Indian Ocean intraseasonal cooling Author(s): VINAYACHANDRAN, PN; SAJI, NH Source: GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Volume: 35 Issue: 23 Published: 2008 Times Cited: 21 DOI: 10.1029/2008GL035733  | added 28-Jul-09 |
| 14. | Title: On the impacts of ENSO and Indian Ocean dipole events on sub-regional Indian summer monsoon rainfall Author(s): ASHOK, K; SAJI, NH Source: NATURAL HAZARDS Volume: 42 Issue: 2 Pages: 273-285 Published: AUG 2007 Times Cited: 19 DOI: 10.1007/S11069-006-9091-0  | added 28-Jul-09 |
| 15. | Title: Statistical Downscaling of Precipitation in Korea Using Multimodel Output Variables as Predictors Author(s): Kang, H.; Park, C. K.; Saji, N. H.; et al. Source: Monthly Weather Review Volume: 137 Pages: 1928-1938 Published: 2009 Times Cited: 19 DOI: 10.1175/2008MWR2706.1  | added 24-May-10 |
| 16. | Title: Intercomparison of the seasonalcycle of the tropical surface wind stress in 17 AMIP atmospheric general circulation models Author(s): Saji, N. H.; Goswami, B. N. Source: Climate Dynamics Volume: 13 Pages: 561-585 Published: 1997 Times Cited: 12 DOI: 10.1007/s003820050183  | added 24-May-10 |
| 17. | Title: Hindcast skill and predictability for precipitation and two-meter air temperature anomalies in global circulation models over the Southeast United States Author(s): Stefanova, Lydia; Misra, Vasubandhu; O’Brien, James; et al. Source: Climate Dynamics Pages: 1-13 Published: 2011 Times Cited: 8 DOI: 10.1007/s00382-010-0988-7  / Author-provided URL : / Author-provided URL :  | added 01-Nov-11 |
| 18. | Title: Evaluation of the Weather Generator CLIGEN with Daily Precipitation Characteristics in Korea Author(s): Min, Y. M.; Kryjov, V.; An, K. H.; et al. Source: Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences Volume: 47 Pages: 255-263 Published: 2011 Times Cited: 7 DOI: 10.1007/s13143-011-0014-y  | added 01-Nov-11 |
| 19. | Title: An improved linear model of tropical surface wind variability Author(s): SAJI, NH; GOSWAMI, BN Source: QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL METEOROLOGICAL SOCIETY Volume: 122 Issue: 529 Pages: 23-53 Published: JAN 1996 Times Cited: 6 DOI: 10.1256/smsqj.52902  | added 29-Jul-09 |
| 20. | Title: SIMULATION OF ENSO-RELATED SURFACE WINDS IN THE TROPICAL PACIFIC BY AN ATMOSPHERIC GENERAL-CIRCULATION MODEL FORCED BY OBSERVED SEA-SURFACE TEMPERATURES Author(s): GOSWAMI, BN; KRISHNAMURTHY, V; SAJI, NH Source: MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Volume: 123 Issue: 6 Pages: 1677-1694 Published: JUN 1995 Times Cited: 6 DOI: 10.1175/1520-0493(1995)1232.0.CO;2  | added 29-Jul-09 |
| 21. | Title: Nonlinear, Intraseasonal Phases of the East Asian Summer Monsoon: Extraction and Analysis Using Self-Organizing Maps Author(s): Chu, Jung-Eun; Hameed, Saji N.; Ha, Kyung-Ja Source: Journal of Climate Volume: 25 Issue: 20 Pages: 6975-6988 Published: 2012/10/01 Times Cited: 6 DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00512.1  / Author-provided URL : / Author-provided URL :  | added 04-Apr-13 |
| 22. | Title: What caused the cool summer over northern Central Asia, East Asia and central North America during 2009? Author(s): Kyung-Ja Ha and Jung-Eun Chu and June-Yi Lee and Bin Wang and Saji, N. Hameed and Masahiro Watanabe Source: Environmental Research Letters Volume: 7 Issue: 4 Pages: 044015 Published: 2012 Author-provided URL :  | added 30-Oct-12 |
| 23. | Title: Accelerating Lagrangian Particle Dispersion in the Atmosphere with OpenCL Across Multiple Platforms Author(s): Harvey, Paul; Hameed, Saji; Vanderbauwhede, Wim Conference: Proceedings of the International Workshop on OpenCL 2013 & 2014 Pages: 1-8 Year: 2014 Author-provided URL :  | added 08-Mar-15 |
| 24. | Title: The role of tropical Atlantic SST anomalies in modulating western North Pacific tropical cyclone genesis Author(s): Huo, Liwei; Guo, P.; Saji, N. Hameed; et al. Source: Geophysical Research Letters Volume: 42 Published: 2015 DOI: 10.1002/2015GL063184  |